6 Educational Philosophies
6 Educational Philosophies 5,7/10 2029 votes
Philosophy of Education
The term “philosophy of education” can be defined in two different ways. According to one definition, the philosophy of education carries out a fundamental philosophical analysis of the forms, methods, aims, meaning and importance of education. Another definition of the term describes or analyzes specific methods of pedagogy.
To put it briefly, the philosophy of education examines how the field of education has connections with the wider sociocultural and philosophical contexts in which it is placed.
Types of Philosophies of Education
6 Educational Philosophies Practice

Spread the loveStudent-centered philosophies are another essential philosophy that educators should be aware of. By focusing on the needs of students, teachers are able to assist and teach students within the classroom ensuring a higher level of student success. In this article three types of student-centered philosophies will be discussed which are progressivism, social reconstructionism,. Educational Philosophy: The Intellectual Foundations of American Education Chapter 6 Philosophy: the study of theories of knowledge, truth, existence, and morality A philosophy of education: A framework for thinking about educational issues, and guide for professional practice-Teacher professionalism: 1) Decision making and reflection 2) A specialized body of knowledge 3) Autonomy 4) Ethical.
There are three main types of philosophies of education – student-centered, teacher-centered and society-centered.
Progressivism (developing a student’s moral compass), Humanism (allowing a student to develop to their fullest potential) and Constructivism (using education to form a student’s world-view) are three examples of student-centered philosophies of education.
Teaching methods of Humanism. Believes education should develope free, self-actualizing person. Believes education should start with self and education should be without coercion.students should make own choices. Education philosophies Perennialism. This is a very conservative and inflexible philosophy of education. It is based on the view that reality. Idealism believes in refined wisdom. It is based on the view that reality is a world within a person's mind. Realism believes in the. Teaching Philosophies and Teaching Dossiers Guide 6 Kenny, Berenson, Jeffs, Nowell & Grant (2018) Introduction Teaching and learning in higher education are inherently complex processes.
Educational Philosophies And Theories
Examples of teacher-centered philosophies of education include Essentialism (teaching basic skills needed to survive in society) and Perennialism (teaching of great works).
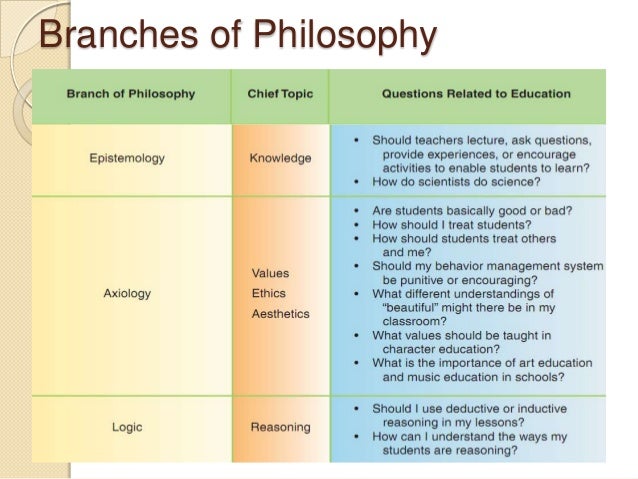
Society-centered examples of education include Reconstructionism (using education to solve social problems) and Behaviorism (cultivating socially beneficial behaviors.)

Major Educational Philosophies
The Importance of Philosophy of Education in Pedagogy
6 Educational Philosophies Articles

In pedagogy, when an individual or a group adheres to a philosophy of education, it means they have a clearly defined set of beliefs, values and opinions regarding education. This constitutes an organized body of knowledge whose theories are put into practice. The philosophy of education that is subscribed to by a school, dictates the subjects or topics, as well as the values and beliefs that students are taught within the core curriculum. This philosophy defines and directs its goals and focus and inspires educational planning.
It is often recommended that the philosophy of education should be a part of teacher education. This is because teachers act as mentors who help their students learn to think independently. However, this is only possible when teachers abide by a teaching philosophy of their own, which they use to inspire their students.
The essays in this list examine the philosophy of education from a variety of perspectives.